Voltage Regulation
Monitor. Register. Control.









What is important for efficient voltage regulation?
Efficient voltage regulation plays a crucial role in electrical power supply, especially when regulating transformers with on-load tap-changers. In general, voltage regulation is about keeping the output voltage of the transformer at a stable level (within the defined tolerance limits) by reacting to fluctuations in the input voltage or load changes. Precise and reliable regulation technology is essential for this purpose.
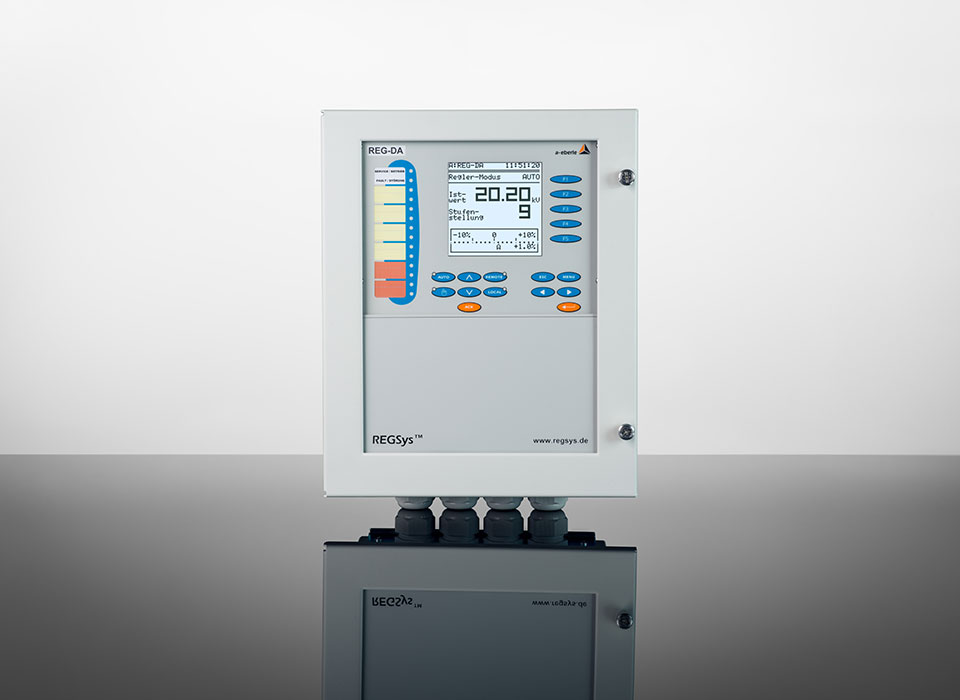
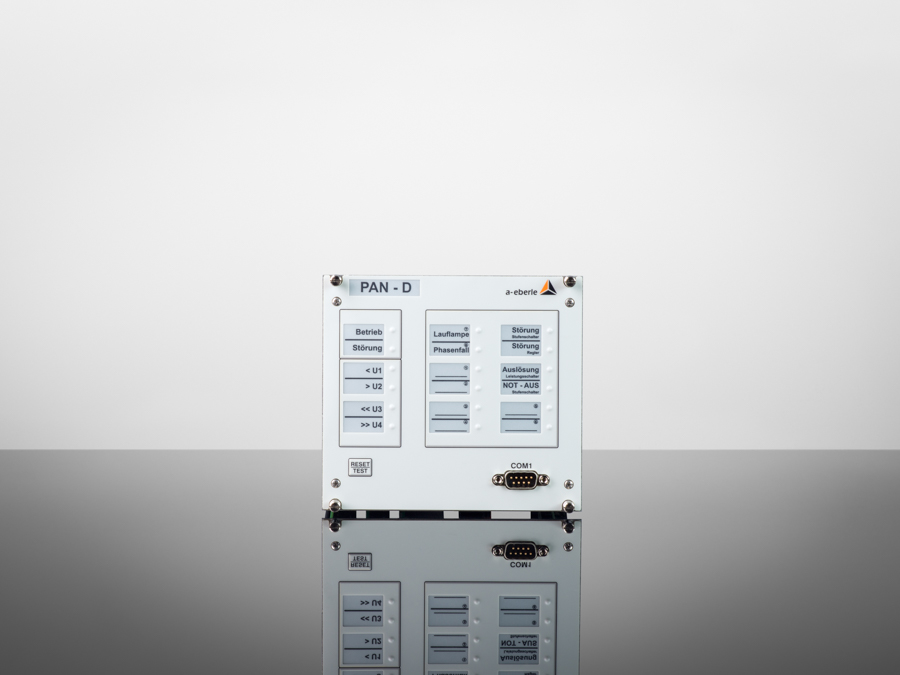
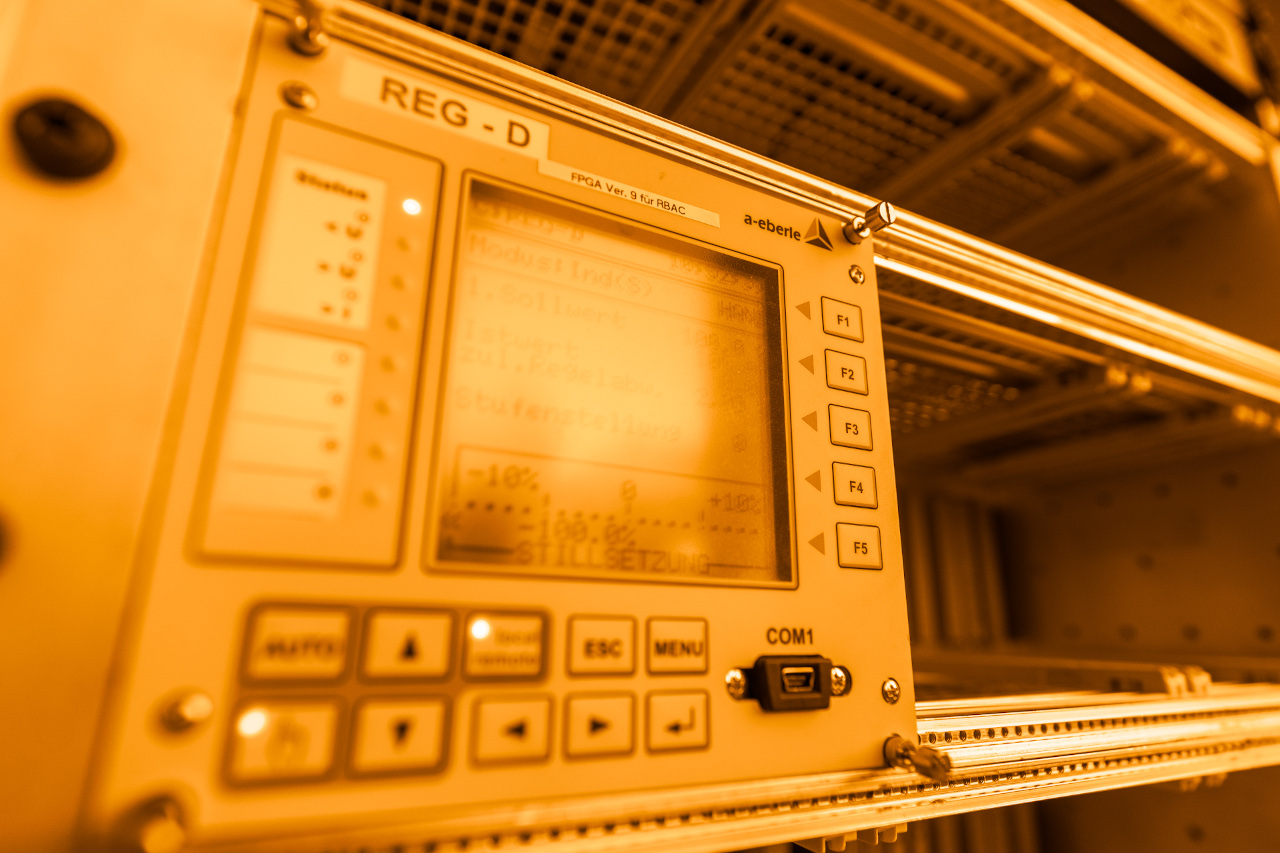
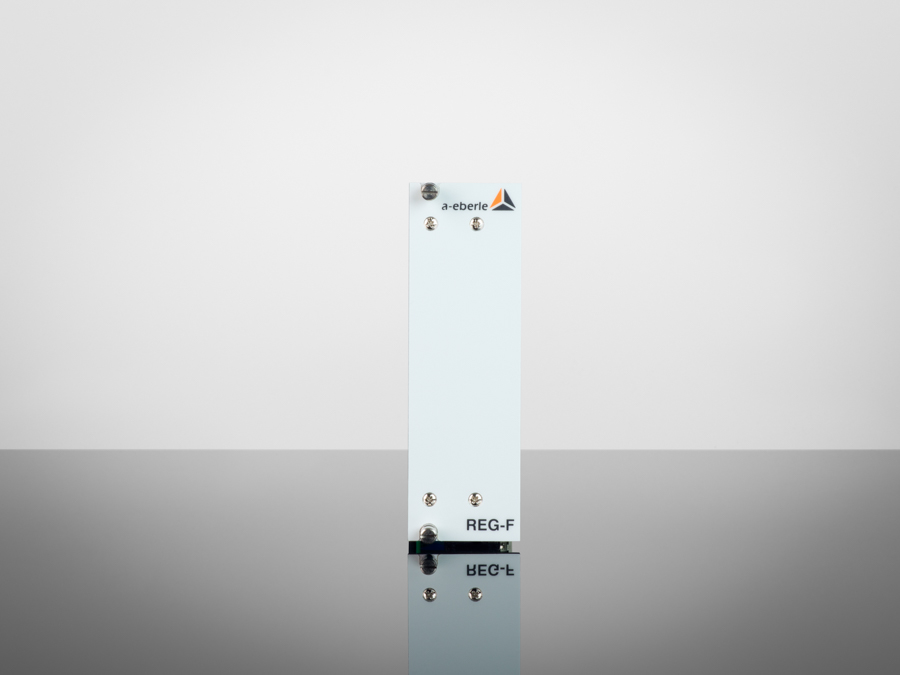
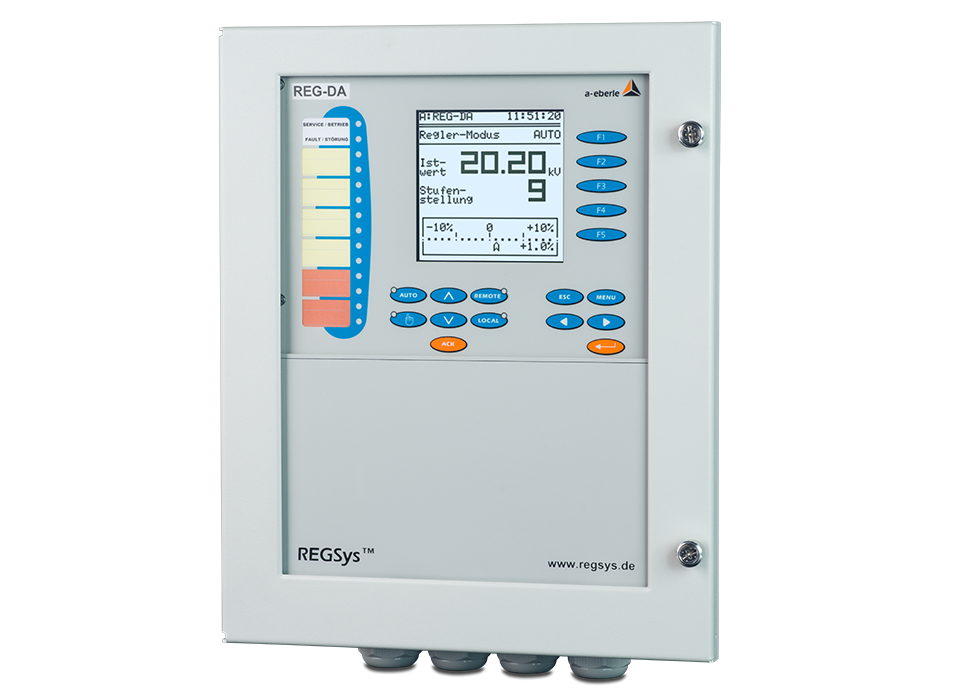
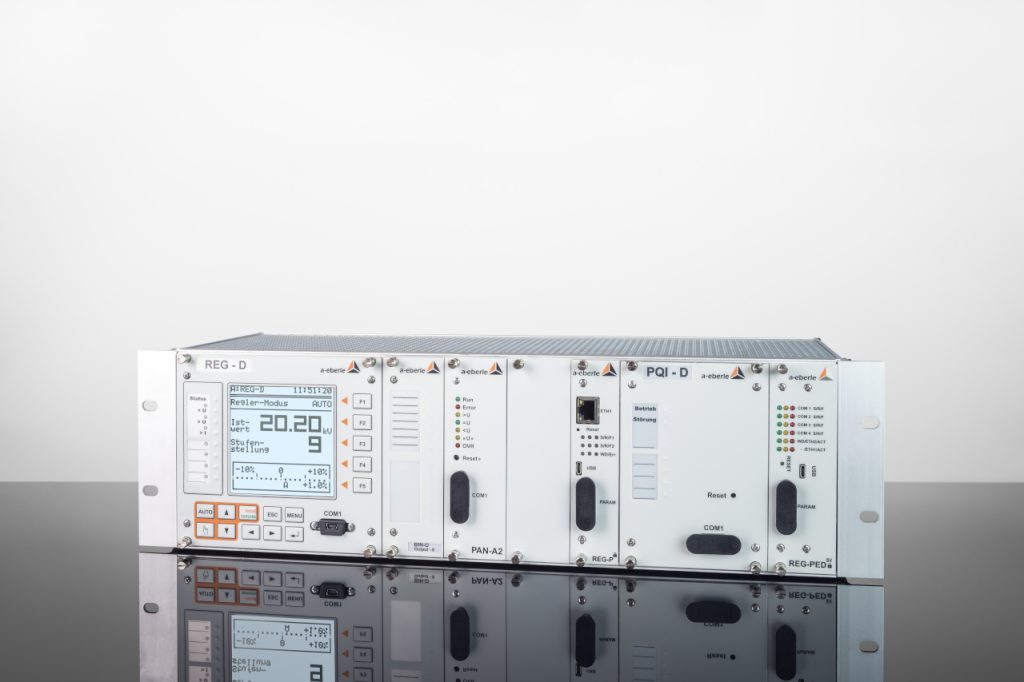
Our »REGSys®« family of voltage regulators, which have been tried and tested thousands of times and are used worldwide, focus on flexibility with regard to customised voltage regulation applications and user-friendliness. The devices continuously monitor the output voltage and adjust it accordingly to achieve and maintain the desired voltage. In addition, the devices of the »REGSys®« family can be easily interconnected to form a regulator network (e.g. parallel operation). The user will find the right solution for every task, at every application.
Our regulators – multifunctional and flexible
Products
Comfortable voltage regulation
With the intelligent additional functions of our »REGSys®« devices
The »REGSys®« voltage regulation system is conceived to allow the regulation and monitoring of tapped transformers in medium- and high-voltage grids & applications.
A wide range of freely adjustable inputs and outputs, display LEDs, smart additional functions – a recorder and logbook, measurement transducer and statistical unit, parallel operation with the »ParaGramer« function, transformer monitoring – and a powerful programming language make this voltage regulation system particularly easy to use.

Which standards define voltage and power quality?

At all voltage levels, there are norms and standards that precisely define and assess voltage and grid quality. In the field of automatic voltage regulation of transformers with tap changers in high and medium voltage, the following standards are particularly relevant:
IEC 60038 (DIN EN 60038)
This standard describes the standard voltage values for electrical power supply and traction current networks, consumer installations and devices.
EN 50160 (DIN EN 50160)
This standard describes the minimum quality of the mains supply, in particular the supply voltage, in terms of frequency, level, waveform and symmetry of the conductor voltages at the transfer point to the customer in public low- and medium-voltage networks.
IEC 61000-2-12
This standard describes the limit values and characteristics of voltage disturbances and signal distortions in electrical supply networks with a nominal voltage of up to 35 kV. It defines specific values and tolerances for parameters such as voltage deviations, harmonics, flicker and signal distortion in order to ensure a stable and reliable power supply.
Virtual Instruction Manual
Description of the basic approach for the
commissioning of our voltage regulator REG-D(A)
MORE Information
Where and when do you need voltage regulation devices?
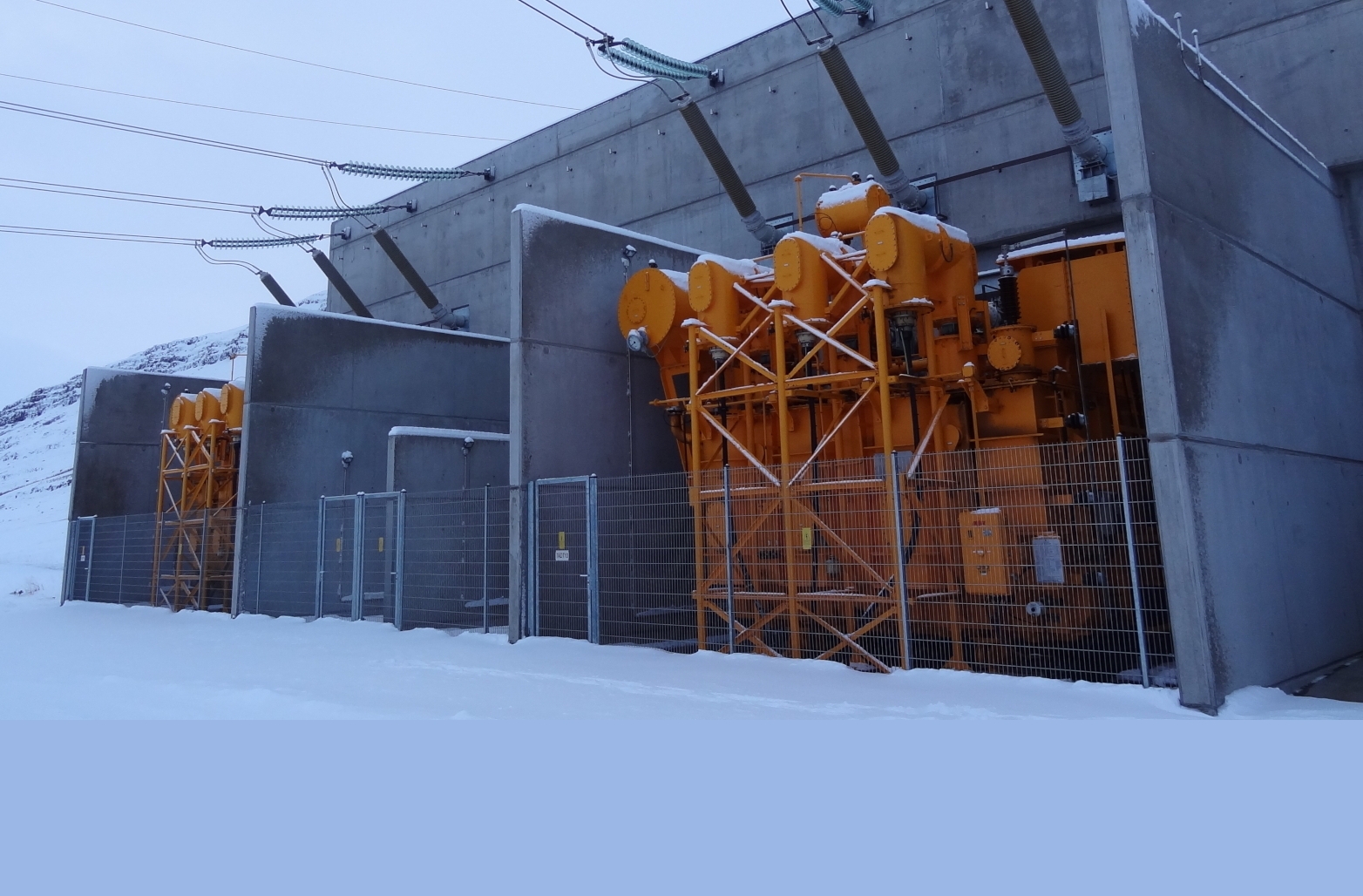
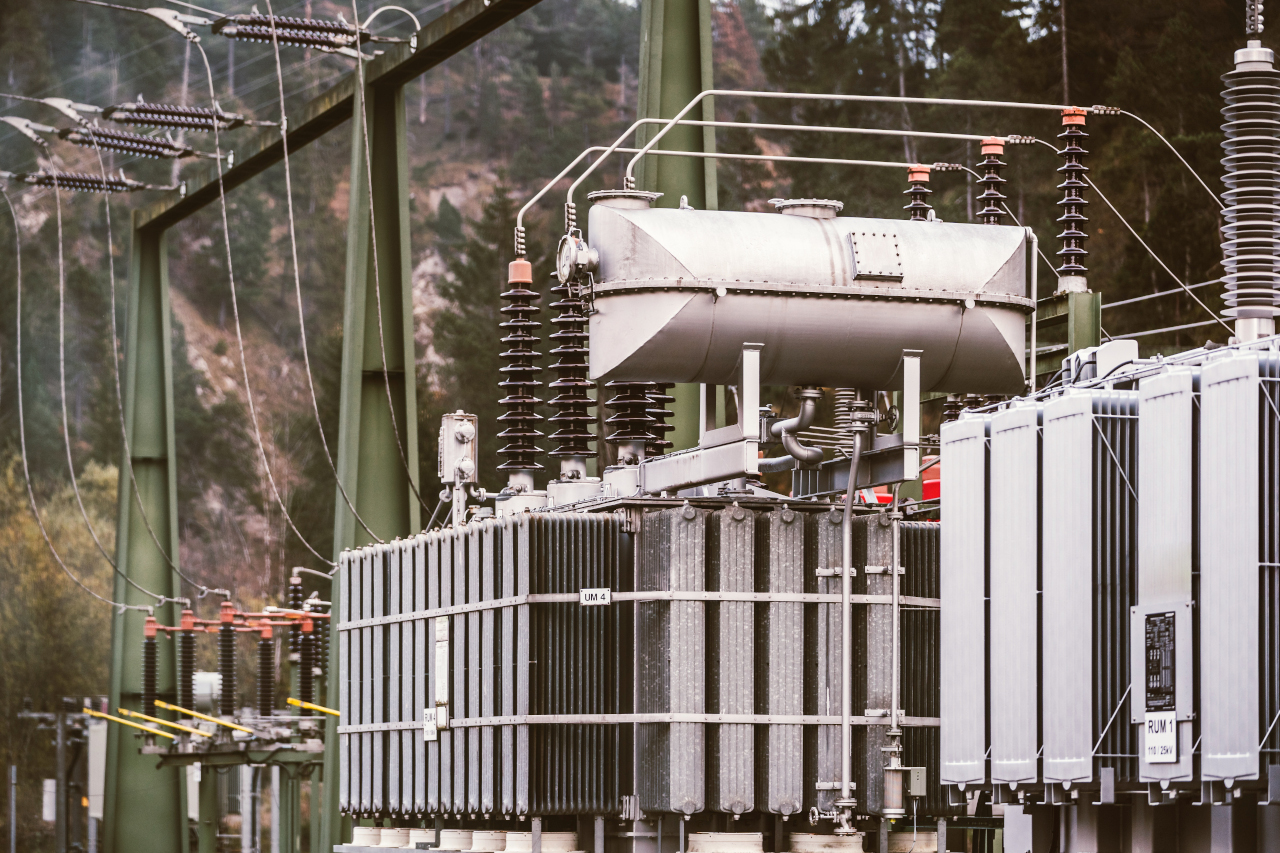
Voltage regulation devices are needed wherever a stable power supply is required, whether in industrial plants, transport, residential areas or the public energy sector. Voltage regulators are particularly indispensable in transformers with tap-changers, which are used for the distribution and transmission of electricity in power grids. They ensure a consistent voltage supply for consumers, which in turn increases the efficiency of the power grid and minimises outages.
In the energy supply sector, voltage regulation of transformers is a crucial step in ensuring a reliable and high-quality power supply. Voltage regulators such as our »REGSys®« voltage regulation system for transformers with on-load tap-changers play a central role for this purpose. Through their continuous monitoring and adjustment, they ensure that fluctuations in the power supply are minimised and the efficiency of the entire energy system is improved.
Design and function of a voltage regulator
What is the function of voltage regulators?
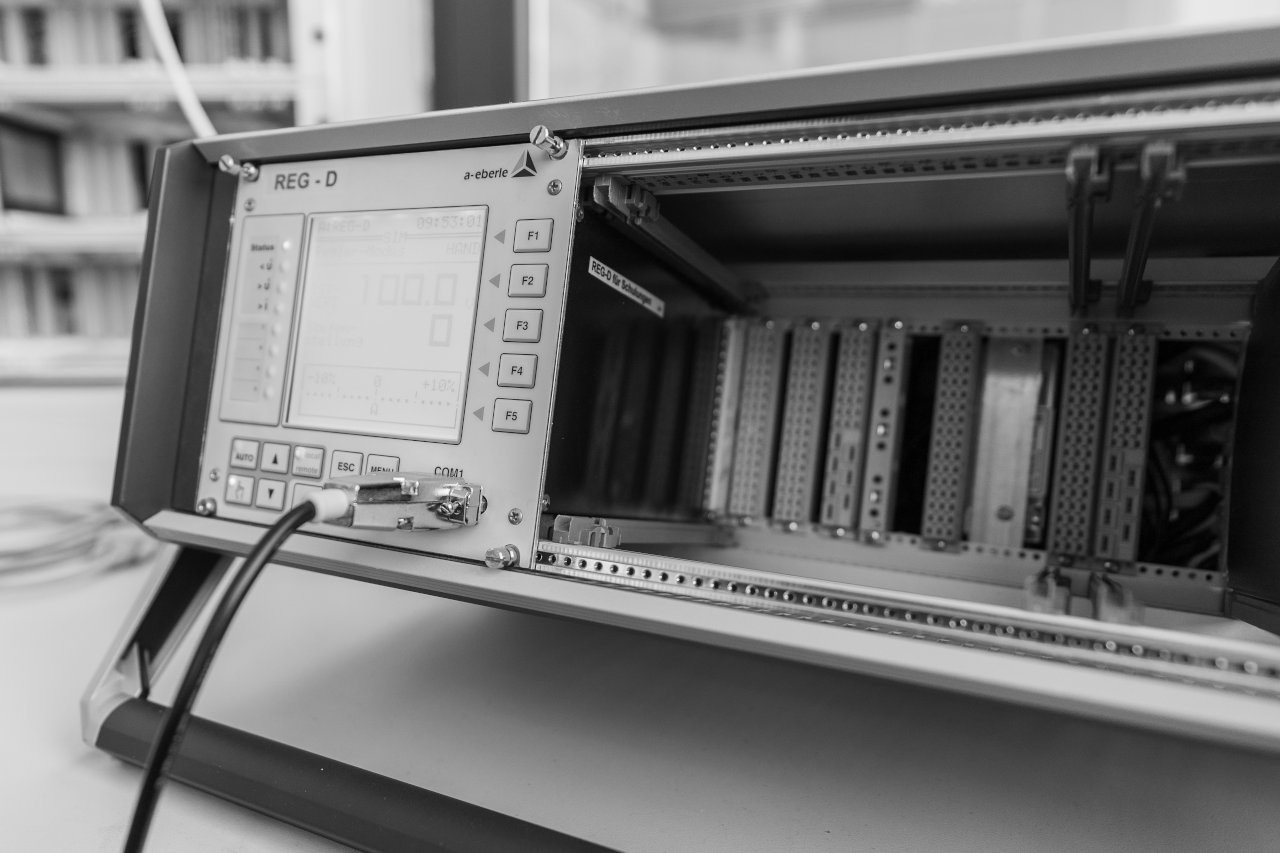
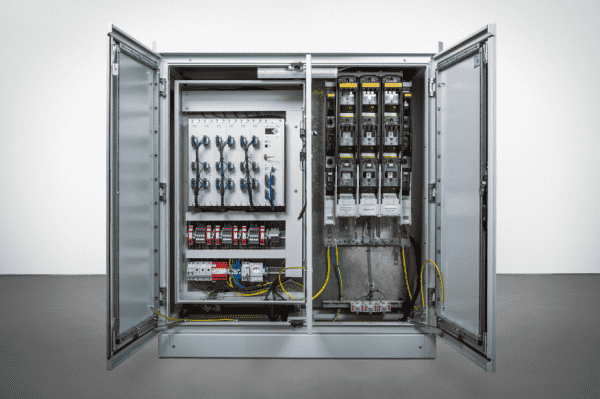
A voltage regulator is a permanently installed measuring/monitoring and regulation device for switching on-load tap-changers on transformers. In order to realise the regulation, at least the current mains voltage is recorded and compared with the set target value. If the deviation between the actual and set value is greater than the permitted tolerance, regulation commands are sent to the on-load tap-changer of the transformer after an adjustable time delay. With our »REGSys®« voltage regulation system, voltage regulation can be supplemented by additional functions such as current influence (e.g. compensation of line impedances) or parallel operation. The measurement of the actual voltage and, if necessary, current values is usually carried out via instrument transformers. The correct function of the on-load tap-changer can be checked via the feedback of the tap position and the running lamp.
How are voltage regulators generally constructed?
The voltage regulator is designed using digital technology. This means that, similar to a PC, the device is based on a processor on which the algorithms and processes required for the regulation process are executed. Either an analogue/digital or digital/analogue conversion or conditioning of the individual signals takes place at the interfaces between the device and the process. The most important signal for voltage regulation is the current measured voltage value. As the voltage regulator is generally used in the medium and high voltage range, the voltage measurement mainly takes place at a voltage transformer. The voltage output by the voltage transformer is transformed again at the measurement input of the regulator and then digitised in an A/D converter.
The voltage regulator has binary inputs to record the tap position, the running lamp and other binary signals. There, the voltage signals are converted into the on or off state by means of a circuit consisting of resistors and optocouplers, which can then be processed by the regulator programme. The tap changer is controlled by relays, which are controlled by the internal algorithm. In addition, the voltage regulator can record process values (e.g. tap position) via standard signals (e.g. -20 to 20 mA) or output them again.

What makes the »REGSys®« voltage regulation system from A. Eberle so special?
Our voltage regulation systems are valued by our customers around the world for their reliability and efficiency. With our »REGSys®« voltage regulation system, we can map the most complex applications precisely to customer requirements and are the global market leader in the field of voltage regulation on transformers with on-load tap-changers. Our devices are characterised by proven technology and precise regulation options and have been specially developed for use in transformers for energy applications in the high and medium voltage range.
Types of voltage regulators: Adjustable voltage regulators
How do adjustable voltage regulators differ from other voltage regulators?
Adjustable voltage regulators (switching regulators) offer the option of manually adjusting the output voltage compared to other voltage regulators. This means that they are more flexible and can provide a variable output voltage that can be adjusted according to application requirements. In contrast, other voltage regulators can have a fixed output voltage that cannot be changed.
For which special applications are they needed?
Adjustable voltage regulators are used in a variety of power supply applications, especially when flexible adjustment of the output voltage is required. For example, they can be used in systems that require different voltage levels or in applications where the output voltage needs to be adapted to changing load conditions. This flexibility makes them particularly suitable for demanding environments where precise voltage regulation is required.
Are voltage regulators from A. Eberle adjustable voltage regulators?
Our »REGSys®« voltage regulation system is an adjustable voltage regulation system. These offer the option of adjusting the output voltage according to the requirements of the respective application, as well as constantly monitoring and supervising the transformer at the same time. Especially in situations where flexibility and adaptability are required, security of supply, optimum performance and high energy efficiency can be guaranteed.
Types of voltage regulators: Longitudinal regulators
How do series regulators differ from other voltage regulators?
Linear regulators belong to the class of linear voltage regulators and are characterised by the fact that they regulate the difference between the input voltage and the stabilised output voltage linearly. In contrast, switching regulators (adjustable voltage regulators) work by switching current paths to regulate the output voltage. Linear regulators, on the other hand, have a simpler design and can also have lower electronic noise interference.
For which special applications are they needed?
Linear regulators are often required in applications where precise and stable voltage regulation is required at lower power levels. Due to their simplicity and efficiency, they are well suited for low to medium power applications, such as regulating supply voltages in the low voltage grid of the electrical distribution network.
Are voltage regulators from A. Eberle longitudinal regulators?
Our »LVRSys®« low-voltage regulation system is a series regulator voltage regulation system. It is characterised by its simple and robust circuitry, which enables precise voltage regulation at lower power levels (7.5 kVA to 630 kVA). »LVRSys®« was developed as a solution to voltage stability problems that arise due to the integration of electromobility, photovoltaics and heat pumps in the low-voltage grid. The system is an economical and flexible alternative to costly and time-consuming line extensions.
Types of voltage regulators: Linear regulators
How do linear regulators differ from other voltage regulators?
Linear regulators are a type of voltage regulator characterised by a simple but effective mode of operation. A distinction is made between cross and linear regulators. In the transverse regulator, the load (the consumer) is in parallel with the regulator circuit, whereas in the series regulator, the controlled system (the so-called series transistor) is in series with the consumer. In contrast to switching regulators, which work by switching current paths, linear regulators regulate the output voltage by adjusting the input voltage linearly. This means that linear regulators allow the voltage to be continuously adjusted by a variable resistor or transistor, which enables precise and stable voltage regulation.
For which special applications are they needed?
Linear regulators are often used in situations where high accuracy and low noise interference are required. Due to their simple operation and their ability to provide a stable output voltage at lower power levels, they are well suited for low to medium power applications, e.g. in the low-voltage network in the power supply of neighbouring strings (hence the term “string regulator”) or industrial companies.
Are (all/some) A. Eberle voltage regulators linear regulators?
Our »LVRSys®« low-voltage regulation system is a linear regulator, or more precisely a longitudinal regulator. The system is characterised by its reliable operation, which enables precise voltage regulation at lower power levels in the low-voltage grid (7.5 kVA to 630 kVA). The system is very popular with our customers all over the world as a flexible, economical and efficient solution for voltage maintenance problems in the low-voltage grid.
Types of voltage regulators: Cross regulator/shunt regulator
How do cross regulators differ from other voltage regulators?
Cross regulators, also known as shunt regulators, work by diverting excess current from the input voltage to stabilise the output voltage. Unlike linear regulators and switching regulators, which regulate the input voltage in different ways, shunt regulators regulate the output voltage by connecting a shunt resistor in parallel with the load resistor. As a result, part of the input current is diverted directly to earth in order to maintain the output voltage.
For which special applications are they needed?
Cross regulators are primarily used in applications where high stability of the output voltage is required and high energy efficiency is to be ensured at the same time. They are particularly suitable for applications with higher outputs where precise regulation and low energy loss are important. Examples of such applications include voltage regulation in high-performance power supply units or in systems with large load changes.
Types of voltage regulators: Automatic voltage regulation/AVR9
What is the difference between automatic voltage regulation and regular voltage regulation?
Automatic voltage regulation (AVR) differs from regular voltage regulation in that it enables continuous monitoring and adjustment of the output voltage in real time. In contrast to static voltage regulators, which are often based on a fixed reference value, AVR reacts to changing conditions in the power grid and dynamically adjusts the output voltage to ensure a stable power supply.
For which special applications is it required?
Automatic voltage regulation (AVR) is particularly needed in applications where continuous and precise voltage regulation is essential to ensure a reliable power supply. It is used in large power grids, substations, hydroelectric power plants, wind farms, industrial plants, data centres, large hospital complexes and other critical facilities where even minor voltage fluctuations can lead to faults, efficiency losses or even outages.
Are (all/some) A. Eberle voltage regulators automatic voltage regulators?
Our voltage regulators of the »REGSys®« family are automatic voltage regulators. They are characterised by their advanced voltagte regulation capabilities and their ability to continuously monitor and adjust the output voltage to ensure a stable power supply. Due to their reliability and efficiency, automatic voltage regulators of the »REGSys®« series are a preferred choice for power supply systems.